Recently, SUSTech Associate Professor Guo Xugang’s group from the Department of Material Sciences and Engineering published their latest research results on all-polymer solar cells (All-PSCs) in Angewandte Chemie International Edition, a top international journal in the field of chemistry (IF=11.994). Titled “Effects of Bithiophene Imide Fusion on the Device Performance of Organic Thin-Film Transistors and All-Polymer Solar Cells”, this work focuses on the design of novel polymer acceptor materials for use in All-PSCs.
As next-generation clean energy source, organic solar cells have attracted much research attention. The acceptor materials used inside are generally fullerene-based small molecules, which suffer from several drawbacks, such as limited tunability of chemical structures and frontier molecular orbital levels, poor light absorption and device stability. With polymer acceptor materials, all-PSCs show great potential in overcoming these drawbacks and to achieve higher power conversion efficiency. Currently, the polymer acceptors are mainly based on imide-functionalized polymer semiconductors, owing to the strong electron-withdrawing capability and good solubilizing ability of the imide group. Among them, polymers based on naphthalene diimide and perylene diimide show the most promising performance in all-PSCs. Developing polymer acceptors with novel structure is much needed to establish the structure–property relationship in all-PSCs and to further improve their performance.
In this work, Professor Xugang Guo’s group synthesized two novel bithiophene imide-based n-type polymer acceptors (Figure 1a). Both materials showed substantial performance in organic thin-film transistors, with electron mobility around 1 cm2 V−1 s−1. However, the small variation in molecular structure led to huge difference in the performance of all-PSCs. The ring fusion of the BTI dimer drastically increased the device performance of the resulting polymer in all-PSCs, with remarkable power-conversion efficiency up to 6.85 % and a large open-circuit voltage of 1.04 V (Figure 1b). This is the best result in all-PSCs that is not based on naphthalene (perylene) diimide type polymers.
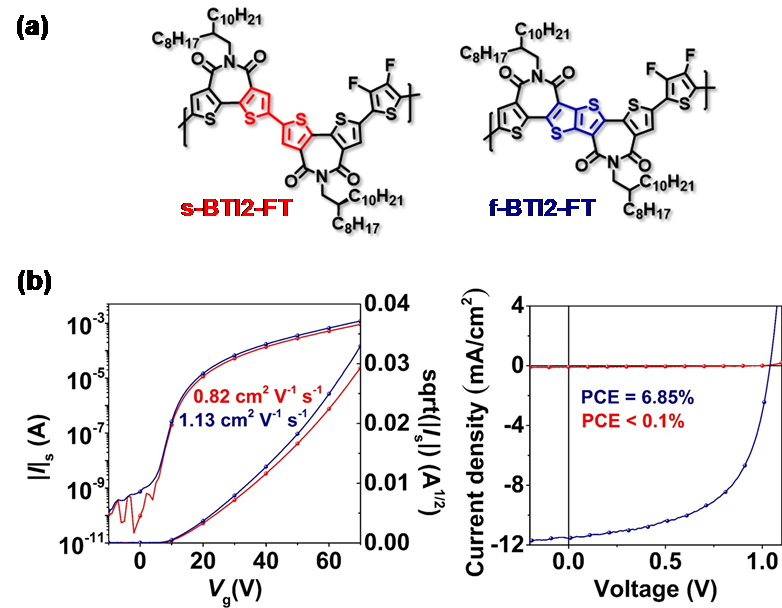
Figure 1. (a) Chemical structures of the two bithiophene imide-based polymer acceptors; (b) organic field-effect transistor performance (left) and all-polymer solar cell performance (right)
Through a series of material and device characterization study, it was found that ring fusion of the BTI dimer led to a narrower band gap, a lower conduction band level, higher planarity and crystallinity in resulting polymer with higher electron mobility. Synchrotron X-ray study showed that ring fusion promoted the formation of favorable molecular packing structures in the polymer semiconductor films, which greatly benefited the charge carrier extraction process, thus larger short-circuit current and higher power conversion efficiency were achieved in corresponding solar cell devices. These research results demonstrate that ring fusion is an effective approach in realizing high performance n-type polymers and provide important guidelines in designing novel polymer acceptor materials.
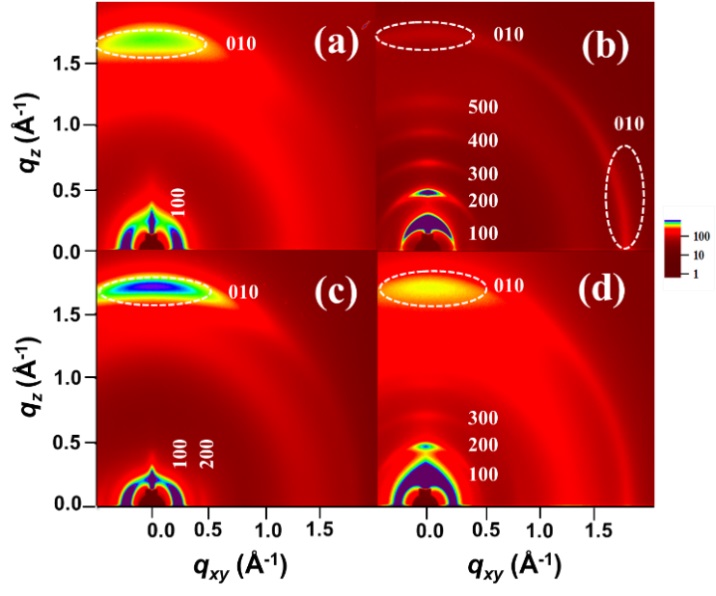
Figure 2. 2D GIWAXS images of the polymer semiconductor films.
Postdoc Wang Yingfeng and master student Zhenglong Yan from Prof. Guo’s lab are the co-first authors of this paper, Research Fellow Guo Han conducted the OTFTs study, undergraduate student Ling Shaohua participated in part of the material synthesis work, undergraduate Xin Zhou performed the DFT calculation. This study was done in collaboration with Prof. Han Young Woo from the Korea University in South Korea (synchrotron X-ray measurement) and Prof. Dai Junfeng from Physics department, SUSTech (optical spectrum study). Financial support was provided by NSFC, Shenzhen Peacock plan, Shenzhen key lab fund, Shiyi fund and several other research grants.
Link to the paper:http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.201708421/full